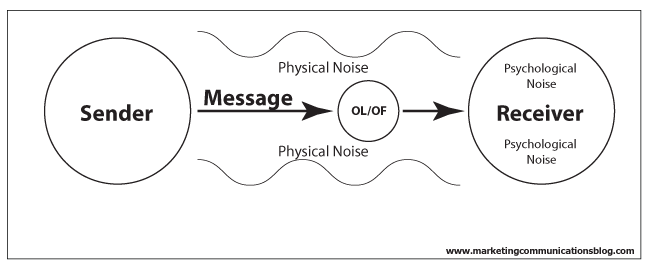
Communication channel is a medium through which a message is transmitted audience,print media or broadcast(electronic) media.Thus, the communication channel refers either to a physical
transmission medium
such as a wire, or to a
logical connection over a
multiplexed medium such as a radio channel.Communicating data from one location to another requires some form of pathway or medium.These path ways are called communication channel which uses two types of media: cable (twisted-pair wire, cable, and fiber-optic cable) and broadcast (microwave, satellite, radio, and infrared). Twisted-pair wire and coaxial cables are made of copper, and fiber-optic cable is made of glass.
Channel models
A channel can be modelled physically by trying to calculate the
physical processes which modify the transmitted signal. For example in
wireless communications the channel can be modelled by calculating the
reflection off every object in the environment. A sequence of random
numbers might also be added in to simulate external interference and/or
electronic noise in the receiver.
Statistically a communication channel is usually modelled as a triple
consisting of an input alphabet, an output alphabet, and for each pair
(i, o) of input and output elements a transition probability
p(i, o). Semantically, the transition probability is the probability that the
symbol o is received given that
i was transmitted over the channel.
Statistical and physical modelling can be combined. For example in
wireless communications the channel is often modelled by a random
attenuation (known as
fading)
of the transmitted signal, followed by additive noise. The attenuation
term is a simplification of the underlying physical processes and
captures the change in signal power over the course of the transmission.
The noise in the model captures external interference and/or electronic
noise in the receiver. If